|
Table of Contents
- What are the most important and most difficult municipal wastewater combust flow and treat decisions?
- Municipal Wastewater Plants to Spend $64 billion for Flow and Treat Equipment This Year
- Municipal Wastewater Decisions System Intelligence database has the support information
What are the most important and most difficult municipal wastewater combust flow and treat decisions?
Mercury removal: The goal of the Municipal Wastewater Decisions service is to assist operators and suppliers with the most important and difficult decisions. It is all part of a concept built around the Industrial Internet of Wisdom (IIoW). Connecting people and knowledge in an organized system is just as important as connecting things. Mcilvaine is creating decision systems around specific industrial processes and specific technologies. An example for a process is municipal sewage sludge incinerator mercury removal Sewage Sludge Incinerator Decisions
The Gore mercury removal module offers an alternative to carbon absorption and has been incorporated in many new incinerator air pollution control systems. The best mercury removal option is in turn related to the choices for particulate removal, organic vapors and acid gases. Therefore the sewage sludge mercury removal decision should be made based on insights from three technology decision systems which Mcilvaine has been compiling for 44 years : 1ABC Fabric Filter; 2ABC Scrubber/Adsorber/Biofilter Knowledge Systems; 3ABC FGD and DeNOx Knowledge Systems; 4ABC Electrostatic Precipitator Knowledge Systems
Cement silo: IIoW needs to break the silo barriers between industries. The municipal wastewater decision makers need to be aware of developments in other industries. For example, sewage sludge can be combusted in solid fuel boilers or cement kilns. One Chinese cement producer is breaking the silo barrier and contracting to handle sludge from municipalities. It optimizes the dewatering and transport condition for the sludge and then directs it to the nearest cement kiln to be used as a fuel. Therefore, the cement mercury removal decisions system becomes relevant. Cement plants have varying quantities of mercury in the limestone used to make cement. So, they already are dealing with the mercury challenge. They now have one new technology to consider which is the catalytic filter to remove acid gases, NOx, and particulate. The catalytic filtration decision guide therefore becomes relevant. The glass industry has standardized on this approach. So, a guide for glass furnace emission control becomes an attractive silo to penetrate.
Natural gas silo: Mcilvaine was hired by Petronas to advise on better ways to remove mercury from natural gas. No novel breakthrough was uncovered. Petronas then decided to fund research in the UK. A new solution using ionic liquid impregnated pellets was developed. It has proven to be a better choice than carbon pellets for natural gas mercury removal. Therefore, municipal wastewater decision makers need to penetrate the natural gas mercury removal silo and see if there are advantages for sludge combustors.
Co-locaton of MWWTP and solid fuel combustors: The solid fuel burning decision silo needs to be penetrated for the huge synergy between municipal wastewater operators and generators of steam and electricity. In the U.S. the average distance between a municipal wastewater plant and an appropriately sized solid fuel combustor is only 70 miles. Many power plants already use treated municipal wastewater for cooling and other purposes. Sewage sludge is often burned in solid fuel combustors. The development of the catalytic filter for solid fuel combustors opens up a new opportunity based on co-location of sewage treatment plants and solid fuel generators. This filter results in clean hot gas at 850F. The heat can be beneficially extracted and used in the co-located MWTTP. One proven application is steam drying of sewage sludge. The sludge from the MWTTP is combusted in the solid fuel boiler and the treated wastewater used by the power plant.
This sewer mining concept dictates the location of an expansion of the MWTTP at a power plant rather than at the existing facility. Sewer mining is already an accepted approach in Australia and some other countries. In Asia where lots of new coal fired boilers and municipal wastewater plants are being built this co=location is particularly attractive. India has a major water problem. So, the co-location is particularly attractive in this country. Much of the technology for this co-location is covered in Coal Fired Decisions.
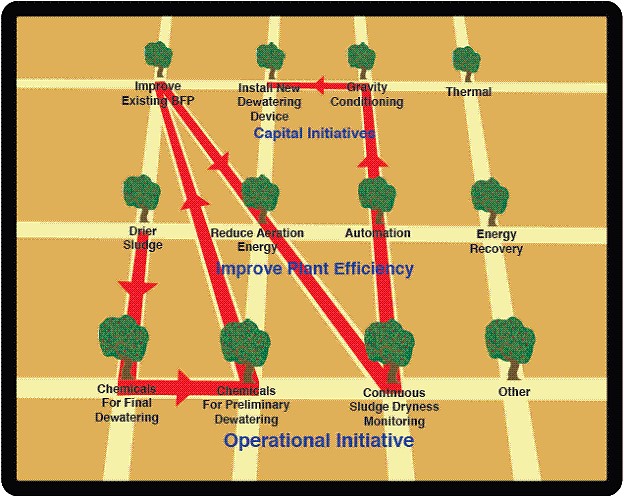
Drier sludge at minimum cost and energy consumption: There are lots of factors in improving energy efficiency in the sludge dfeatering process. For WEBTEC 2013 Mcilvaine created a Global Decisions Positioning System to guide visitors seek to address this problem. It included stops at the relevant exhibition stands and attendance at the relevant papers.
Aeration Blowers There is an aeration blower decision guide which is being continually updated Aeration Decisions.. This analysis compares the performance of all the different blower types over a range of applications. Here are some of the important preliminary conclusions:
- Larger blowers are being replaced with multiple smaller ones which better address the fluctuating loads
- Turbo blowers and low pressure screw compressors are gaining market share
- Energy efficiency incentives are being offered in Asia and Europe as well as the U.S.
- Electricity costs in many countries are twice as high as the U.S
- Third party operators have a big incentive to reduce energy costs
- More plants are operated by third parties in Asia than in the U.S.
- The design of the aeration system has a big influence on blower sizing
- The large majority of blower purchases worldwide are for replacement of either just the blower or the whole system. A relatively small % of the blower purchases are in countries with the largest growth percentages for treatment additions. Therefore the U.S. and countries with large treatment capacity remain the big markets
Treatment Chemicals: Polymers to dewater sludge are a big expenditure. As per the diagram above there is a balance needed to provide the best combination of dewatering chemicals and equipment. A filter press and less chemicals can be compared to centrifuge or belt press and more chemicals. The use of treated municipal wastewater for industrial purposes has created decision requirements for anti-scalants in the RO systems conditioning municipal wastewater for industrial use. Corrosion control is needed if secondary wastewater is going to be used in cooling towers.
Odor Control: The decisions regarding odor control for municipal wastewater plants are challenging because
- Odor control problems extend from the lift station to the treatment plant and the many treatment processes
- A wide range of odor causing compounds are likely
- Odors comprise the most neighborhood complaints
- Odor measurement is subjective and not quantitative
- Many technology options are available which complicates the choice
- Capture of the ambient odors with the highest efficiency and lowest amount of air is challenging
- There are choices between options for treatment of the waste to avoid odor emission vs treatment as an air contaminant
Mcilvaine has decision systems on air monitoring and also on scrubbers, adsorbers, absorbers and biofilters which have been continuously updated since the late 1970s. 1100 articles on odor control are included in the Scrubber Adsorber intelligence system. Here are some article titles and key factors:
Evoqua Introduces New WHISPER™ Biofilter System for Quiet and Effective Odor Control in Residential Locations Key factors: 99% H2S removal at up to and exceeding 100 ppm, efficient nutrient removal, variable speed fan, turnkey service and monthly rental
Bionomic’s Latest Edition Series 5000 Packed Tower Scrubbers Are Match Engineered to Precisely Meet the Most Demanding Gaseous Contaminant, Odor Reduction, Mist Removal, and Process Requirements. Factors: ability to match packing selection to the site specific conditions
PRD Tech’s Biotrickling Filter Controls Odors: Factors: biotrickling filter vs just biofilter or alternatives
Here Is the comparison provided by KCH
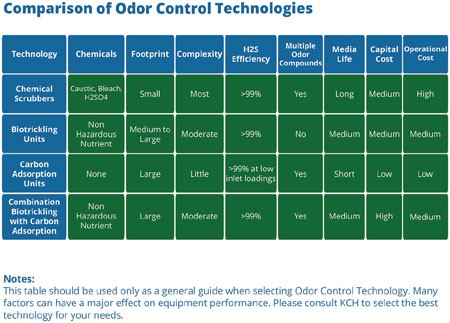
Here is the comparison of biotrickling and biofiters by Envirogen: Biotrickling Filters are vertically-oriented vapor-phase bioreactors filled with an inorganic media featuring 100% recirculation. The filters’ unique design can address high concentration of H2S odors in areas where space is at a premium – offering a shorter retention time and treatment of higher air volumes than conventional biofilters. They can also treat high concentrations of VOCs and ammonia, and be chemically augmented when needed.
The decision system for odor control in municipal wastewater plants is supported by decision guides on scrubbers, adsorbers, monitoring, and ventilation design as well as for H2S treatment of liquids to prevent emissions.
IIoT and Remote O&M: MWTTPs can greatly reduce cost of operations through the use of the Industrial Internet of Things empowered by the Industrial Internet of Wisdom which includes the decision guides. Detailed coverage of this opportunity is provided in a free recording https://youtu.be/AWB-vZIj5gk
A free webinar to discuss the municipal wastewater flow and treat market and the sea change in the way purchasing decisions will be made will be held at 10:AM Central time on the March 28. To register click on Free Market Webinars
Municipal Wastewater Plants to Spend $64 billion for Flow and Treat Equipment This Year
Municipal wastewater treatment plant operators world-wide are anticipated to spend $64 billion for selected flow and treat products and services this year. The majority of these purchases will be made by just 200 operators and 30 engineering/consulting firms.
Suez is supplying more than 30 million people with water and wastewater services. They are also designing plants and purchasing flow and treat products for new as well as existing plants. Beijing Enterprises Water Group (BEWG) operates more than 400 wastewater plants in China and other countries and is also involved in design build projects where they would specify flow and treat products. Chicago MSD operates seven wastewater reclamation plants. It is also expanding its scope by encouraging nearby food processors to send waste to the plant for conversion to biogas. This will increase its sludge processing, compressor and air pollution control purchases. Los Angeles Sanitation’s operations are approximately half the size of those in Chicago.
|
2018 Municipal Wastewater Purchases
$ millions
|
| |
World
|
U.S.
|
Suez
|
Jacobs
CH2M
|
BEWG
|
Los Angeles
|
Chicago MSD
|
| Guide |
5280 |
1100 |
106 |
63 |
33 |
11 |
22 |
| Control |
8640 |
1800 |
173 |
104 |
54 |
18 |
36 |
| Measure |
4320 |
900 |
86 |
52 |
27 |
9 |
18 |
| Valves |
4800 |
1000 |
96 |
58 |
30 |
10 |
20 |
| Macrofiltration (belt presses, sand filters) |
2400 |
500 |
48 |
29 |
15 |
5 |
10 |
| Pumps |
9600 |
2000 |
192 |
115 |
60 |
20 |
40 |
| Treatment Chemicals |
6720 |
1400 |
134 |
81 |
42 |
14 |
28 |
| Sedimentation and Centrifugation |
4320 |
900 |
86 |
52 |
27 |
9 |
18 |
| Variable Speed Drives and Motors |
4800 |
1000 |
96 |
58 |
30 |
10 |
20 |
| Turbines, Fans, and Compressors |
10560 |
2200 |
211 |
127 |
66 |
22 |
44 |
| RO/UF/MF Cross Flow Membrane Systems |
1200 |
250 |
24 |
14 |
7 |
3 |
6 |
| Air Pollution Control |
960 |
200 |
19 |
12 |
6 |
2 |
4 |
| Total |
63,600 |
13,250 |
1271 |
765 |
397 |
133 |
266 |
McIlvaine is forecasting flow and treat product and service expenditures for all industries and for 550 operating companies and 400 OEMS, EPCs and process sub system companies worldwide. Municipal wastewater is one of 14 industries which are covered. The wastewater purchases in many countries are concentrated among just a few operators. Suez operates more than half the plants in Chile. In the U.S. the engineering/consulting firms play a big role.
There is a metamorphosis in the way purchases will be made in the near future. Process management system suppliers are providing monitoring and control of every valve, pump and filter from remote monitoring centers. Suez is monitoring hundreds of plants from its European base. The equivalent of millions of total lowest cost of ownership analyses are continually generated. This development will profoundly change the route to market as explained in N031 Industrial IOT and Remote O&M.
Profiles of the 100 largest operators and EPCs worldwide are included in 62EI North American Municipal Wastewater Treatment Facilities and People Database which is being expanded to include the major worldwide purchasers.
A decision system for municipal wastewater flow and treat purchases includes a number of decision guides. One is on aeration blowers. Another system provides the odor control options. There is a guide just on mercury control options for sewage sludge incinerators Details are found at Municipal Wastewater Decisions.
Detailed forecasts for each of the 550 major purchasers are shown in the relevant market reports listed at http://home.mcilvainecompany.com/index.php/markets
Municipal Wastewater Decisions System Intelligence database has the support information
Case histories and papers are being uploaded to the intelligence system. Here are some samples:
Advantages of new Kaeser rotary screw blower package
In addition to many advantages cited in the article, the rotary screw blowers are available with variable speed control managed by the Kaeser Sigma Control 2™ system. This advanced controller comes standard with multiple pre-programmed control profiles so wastewater treatment plants can select the one best fitting their application. The control system monitors more than twenty critical operating parameters on each unit. Many if not all aeration blower applications require a total system controller. Kaeser’s Sigma Air Manager (SAM) can control up to 16 blowers and only turn them on as needed. The SAM system allows the blowers to be controlled based on dissolved oxygen levels or other WWTP performance targets. While the desired levels of DO, NH4 and NO3 remain the same, the amount of air required to maintain those levels varies based on a wide range of factors such as ambient temperature and humidity. The SAM system automates and optimizes the blower’s wire-to-air efficiency while delivering the required oxygen.
Revision Date: 12/29/2017
Tags: 221320 - Sewage Treatment Facilities * , Kaeser Compressors, Inc., Blower, Controls
Neuros blower performance evaluated by CDM at Franklin, N.H.
The advantages of high speed turbos compared to PD blowers were analyzed bases on a demonstration by Neuros. 32 % higher efficiency was demonstrated by the direct drive unit and close to 50% higher efficiency achieved with D.O monitoring and control.
Revision Date: 12/29/2017
Tags: 221320 - Sewage Treatment Facilities * , Camp Dresser & McKee, Blower, Aeration
Multi stage centrifugals replaced at City of Altamonte Springs, FL
• The City of Altamonte Springs Regional Water Reclamation Facility (RWRF) has a permitted design capacity of 12.5 million gallons per day (MGD) on an average annual daily flow (AADF) basis. The current AADF is approximately half of the permitted value and the facility maintains consistent compliance with regulatory agency permit requirements related to effluent quality. • takeaways • Older multistage centifugals replaced with more efficient selections • Either turbo or rotary blowers recommended for the process • Concerns about complexity of turning down volume with multi stage centrifugal • Install centralized aeration control system • Rotary blower with VFD recommended for aeration in sludge holding tank where load fluctuations offer potential for energy savings.
Revision Date: 12/15/2017
Tags: 221320 - Sewage Treatment Facilities * , Tetra Tech, Aeration Blower, Blower, Aeration
High speed blowers for Garland Texas wastewater
High speed blowers were installed at Garland Texas and reduced energy consumption compared to the previous multi-stage blowers. The control system has been optimized to utilize several blowers in the most efficient manner. The high speed blowers had a higher initial cost but a 2 year payback on energy savings.
Revision Date: 12/15/2017
Tags: 221320 - Sewage Treatment Facilities * , Perkins Engineering Consultants, Aeration Blower, Blower, Aeration
Activated Sludge Plant Study Guide
Study guide prepared for educators and operators provides useful background information on factors affecting choice of aeration components.
Revision Date: 12/6/2017
Tags: 221320 - Sewage Treatment Facilities * , AECOM, Aeration Blower, Blower, Aeration
Process simulator evaluates blower and valve control strateigies This paper will introduce the process of calculating and incorporating pressure
This paper will introduce the process of calculating and incorporating pressure losses, blower speed and valve positioning into the activated sludge model simulation, quantify the control response for conventional and innovative control strategies, and demonstrate the benefits of flow-based blower control schemes versus pressure-based blower control. The design of the aeration system has become one of the most important aspects of the design of the activated sludge process, but process engineers only have commercially available process simulators with activated sludge and aeration models to calculate dynamic process requirements, not the actual equipment requirements for an aeration system. It was demonstrated that the process of calculating and incorporating pressure losses, blower speed and valve positioning into the activated sludge model allows the engineer to see them change as the influent process conditions change diurnally and seasonally, so equipment can be sized accordingly. Using the combined models for control valve sizing, estimating the pressure requirement for the blower, and comparing the dynamics of three different types of aeration control methods was also demonstrated. At this point, the aeration system model could not be compared to actual operational data. A comparison would be valuable, and should be done to determine the overall accuracy of the model. However, the valve, blower and pressure models were developed using methods already used in design, which gives confidence that the models as used in the paper would provide an accurate design tool.
Revision Date: 12/6/2017
Tags: 221320 - Sewage Treatment Facilities * , BioChem Technology, Software, Blower
Rohm and Haas reduces aeration costs through optimization
Rohm and Haas Company was able to drastically reduce O&M costs for their Aeration System by focusing on Reliability Engineering and Optimization at their WWTP. The costs reductions were a team effort and have resulted in a wide variety of benefits for Rohm and Haas and for the people associated with the WWTP. This initiate also revealed several interesting points relating to the design and operation of WWTPs: • Good data, particularly D.O., air flow and blower amps can help optimize operations and reduce energy costs. Without this data, plants may be wasting energy unnecessarily by adding to much air. • Existing blowers may be operating very inefficiently even if they are throttled or controlled to maintain D.O. setpoints. • If plants are designed for conservatively high present or future peaks loadings, the result will be an inefficient operation with oversized components unless good turndown is incorporated into the design. If designing for peak conditions, the use of different size blowers is strongly recommended.
Revision Date: 12/5/2017
Tags: 325000 - Chemical Manufacturing , Rohm and Haas Company, Optimization, Blower, Aeration Blower, Aeration
Wide Variety of Valves for Water and Wastewater Treatment Plants
This 8 page listing includes details on gate valves in various different size ranges. Here is just the specification for the small valves. Gate Valves 1-1/2 Inches in Diameter and Smaller: 125 psig; bronze; rising-stem; single-wedge; disc type; screwed ends; such as Crane No. 428, or approved equal. Coatings for Gate Valves 2 Inches and Larger: AWWA C550; Indurall 3300 or approved equal, non-toxic, imparts no taste to water, functions as physical, chemical, and electrical barrier between base metal and surroundings, minimum 8-mil-thick, fusion-bonded epoxy. Prior to assembly of valve, apply protective coating to interior and exterior surfaces of body. The specification also includes plug valves, butterfly valves, air release and pressure reducing valves. Many of these valves are general performance valves sold primarily by price. However, a number of valves used in slurry lines and for sensitive control are high performance valves sold on the basis of lowest total cost of ownersh8ip. We will endeavor to identify those applications and pursue cost of ownership aspects for them.
Revision Date: 12/5/2017
|